Rigid-Chain Technology for Today's Die-Change Challenges
October 1, 2019 While the basic system itself was developed nearly a half-century ago, today's rigid-chain iterations are as numerous as
die-design challenges.
|
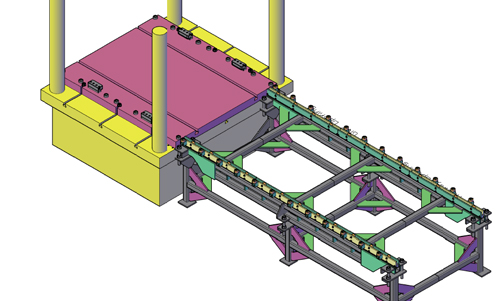
| A table-mounted push-pull system allows for the elimination of wandering and popping. Such systems can be sized for large loads, with swing-aside bolster extensions creating an aisle between the press and die-change table. |
More than 45 yr. ago, toolmakers developed the rigid-chain system used today for quick die change (QDC). Such systems have ‘shoulders’ that interlock when laid out flat, creating a column that can push loads. Many different rigid-chain configurations allow for application-specific solutions to many die-change challenges. The key solutions using rigid chain, and their advantages and disadvantages, are presented here.Press-Mounted Push-Pull Systems
Description: System integrates into the press.
Advantages: Pulling against V-block location devices minimizes chain size, as pushing against hard stops with excessive chain stroke can cause the chain to wander or pop.
Disadvantage: Dedicated equipment can be used only on one press.
Table-Mounted Push-Pull Systems
Description: Mounted table, usually on some type of roller bars or lifters for smooth movement.
Advantages: Allows for the elimination of wandering (side-to-side movement of the chain as it moves forward) and popping (when the chain does not stay down during the whole length of the stroke). Such systems can be sized for large loads, and swing-aside bolster extensions create an aisle between the press and die-change table.
Disadvantages: Requires dedicated floor space and there is no prestaging of the die.
Rail-Mounted Die-Cart Systems
Description: Rails, embedded in the floor, enable the movement of die carts.
Advantages: Adds flexibility to the die-change process, allowing dies to be positioned in a crane bay different from the press (i.e., transfer die from press to coil car area where crane capacity could be vastly different). A dual-cart design allows for pre-staging die, externalizing the die-change process.
Disadvantages: The installation of rails involves excavation. Rails must be clear of items when in use.