Hot Potato
|
 |
|
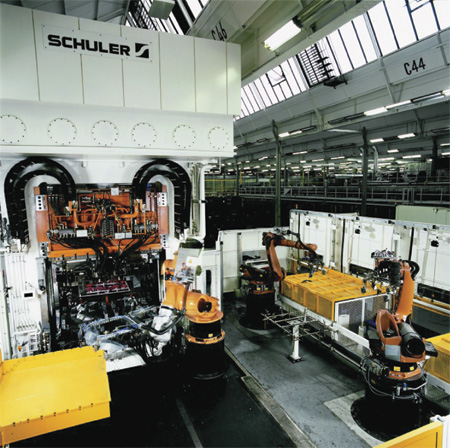
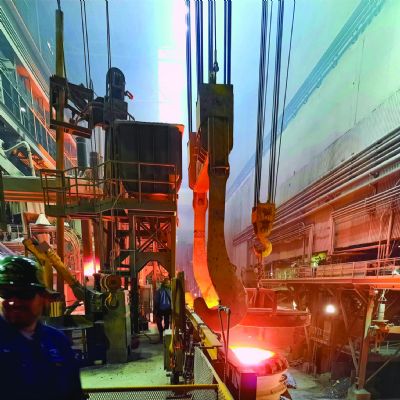
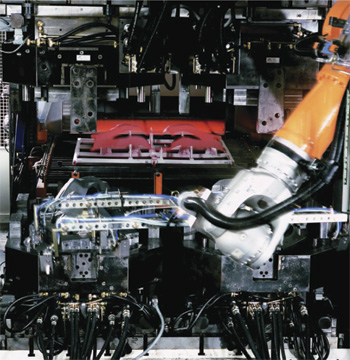
| These photos from Schuler showcase a robot-tended hot-stamping line and the feeding of heated blanks into the die. | |
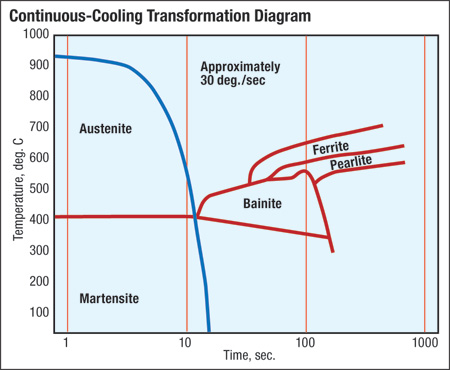
After exiting the oven, each heated blank transfers to a hydraulic press via robot or pick-and-place mechanism. At this stage the blank has a strange muted glow to it as it settles into the lower die section. The press closes tightly to clamp the die shut at a relatively high tonnage—not so much for the forming process but for the need to create an extremely tight bond between the die surfaces and the part. The die is permeated with channels in its upper and lower sections, designed to distribute cooling water throughout. The tightly closed die functions as a heat sink, absorbing the heat from the part. The blank cools quickly, within seconds, by several hundred degrees until it reaches the martensite phase. This results in a lightweight blank with phenomenal strength characteristics.
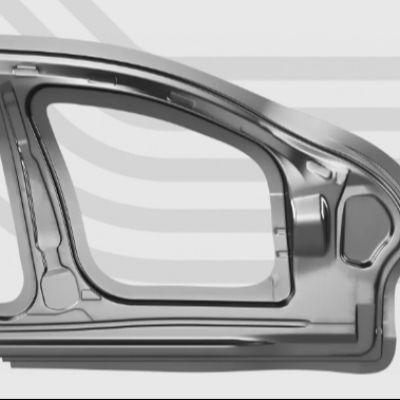
Cool the blank too slowly and it will enter the bainite, ferrite or pearlite phases and exhibit out-of-spec properties. Conversely, by controlling the cooling process in the die, it is possible to create hot-stamped parts exhibiting various strength characteristics throughout their length. This proves critical in applications requiring a part to crumple in one area while maintaining stiffness in another, such as an automotive safety pillar.
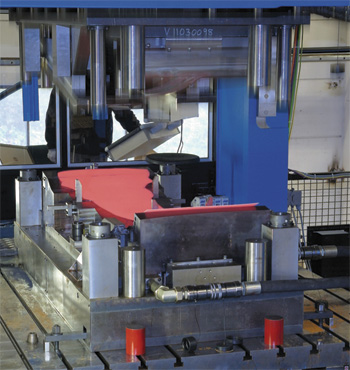
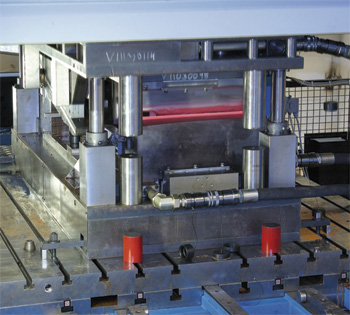
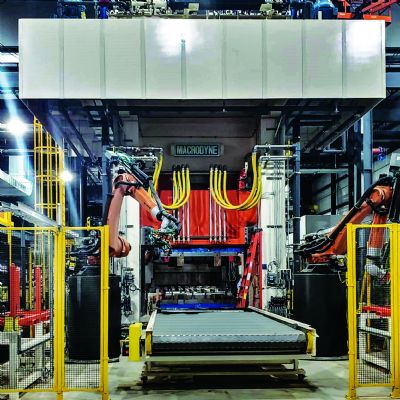
Dies open and closed, stationed in an AP&T hot-stamping line. The closed die performs forming and cooling functions.
After a few seconds, the die opens and the automation device removes the part from the die and places it on a rack. Blank trimming typically is performed by laser cutting; alternative trimming techniques also are used.
The most engineering- and design-intense part of the entire process is the die. The die designer must be thoroughly familiar not only with conventional design and simulation software, but he also must be fluent with thermal-simulation software. Such software might include metallurgical-simulation software for the understanding of the metallurgical transformations of a particular part within the die. Other critical success factors include design of the cooling channels and the chiller, and the use of sensors to monitor performance.
Opportunity Knocks
Now let’s explore the potential economic opportunities hot stamping offers Tier Two and Three stampers. I am convinced that it is simply a matter of time before sectors other than automotive will adopt hot stamping to remove weight from, while strengthening, their products. Who would not want a lighter and stronger lawn mower? What about replacing machined or cast parts with hot-stamped parts? And how about the aerospace industry, where strength and weight als are a concern? Perhaps parts currently stamped from exotic materials such as titanium or magnesium alloys could be candidates for hot-stamped steel parts instead.
But how to pay for that first hot-stamping line? There are various grants available to help offset the costs of research and development in manufacturing. Your state likely offers such a program, a perfect opportunity to obtain at least partial funding for an experimental hot-stamping line that would allow a stamper to approach RFQs from current and potential clients for hot-stamped parts. Similar programs abound within the federal government. Such an experimental setup would allow a stamper to revisit current cold-stamped parts and perhaps develop viable and lucrative alternatives.
In other words, I see hot stamping as allowing metalformers to take quantum leaps over their competition by opening up new markets for their companies. During the week of December 5, I will conduct the Big Sky Manufacturing Conference in Germany. Designed for North American metalforming executives not currently running hot-stamping lines, the event will afford the opportunity to visit German stamping shops running cold-forming lines as well as hot-stamping lines. For more information, visit www.mfgadvice.com. MFView Glossary of Metalforming Terms
See also: Tecknow Education Services, Inc.
Technologies: Stamping Presses







 In 1776, Thomas Paine described the fledgling American experiment in independence as, “These are the times that try men’s souls.” Today’s economic uncertainties likewise tug mightily at the corporate ranks, as metalformers of all sizes seek a more secure path through the economic thicket. Our industry needs a technological jolt to innovate its to prosperity; this is especially true for Tier Two and Three suppliers of metalformed parts.
In 1776, Thomas Paine described the fledgling American experiment in independence as, “These are the times that try men’s souls.” Today’s economic uncertainties likewise tug mightily at the corporate ranks, as metalformers of all sizes seek a more secure path through the economic thicket. Our industry needs a technological jolt to innovate its to prosperity; this is especially true for Tier Two and Three suppliers of metalformed parts.



