When it comes to the implementation of Industry 4.0 principles, Mathews opines that many manufacturers still struggle with disconnected data systems, limiting their ability to optimize operations. “The concept of a unified digital thread is gaining traction as platforms integrate design, production and machine data in real time,” explains Mathews. “This connectivity provides end-to-end visibility, driving agile responses to market demands and improving quality.
“For example, linking manufacturing execution systems (MES) with material requirements planning software facilitates seamless communication between shop floors and offices,” Mathews continues. “These systems empower manufacturers to eliminate inefficiencies and make data-driven decisions.”
For many manufacturers, especially small and mid-sized enterprises, a fully connected digital thread may still feel out of reach. However, incremental steps can yield immediate benefits, Mathews suggests, setting these enterprises up for a future of full connectivity.
“For instance, implementing sensors on critical equipment and connecting them to MES software can provide real-time insights and improve job tracking,” Mathews says. “These small changes build confidence and demonstrate a return on investment, encouraging further investments in digital transformation.”
 Finally, the pairing of AI and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming predictive analytics in manufacturing. These technologies enable manufacturers to anticipate equipment failures, optimize energy usage and streamline supply chains.
Finally, the pairing of AI and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming predictive analytics in manufacturing. These technologies enable manufacturers to anticipate equipment failures, optimize energy usage and streamline supply chains.
“In the automotive sector, AI-driven digital twins enhance predictive maintenance and reduce downtime,” Mathews says. “Similarly, in the medical sector, where precision is critical, predictive tools improve quality and minimize waste.
“While Industry 5.0’s vision of human-centric sustainable manufacturing is inspiring,” Mathews continues, “many manufacturers still are adopting Industry 4.0 principles, such as going paperless on the shop floor. For these businesses, we’re starting to see incredible incremental progress. Digitizing maintenance logs, deploying basic AI tools for operational or machine-specific insights, and experimenting with digital twins can be practical first steps. The focus should be on aligning solutions with the most immediate needs for efficiency, while building toward a more connected future.”—BK
Issues Aplenty Cloud Automotive Outlook
An uncertain future exists for automobile sales in an industry that rolls most smoothly with all wheels on the ground. Macroeconomic factors pull the industry to both sides of the road. The rate of inflation has cooled, but the threat of new tariffs looms. Interest rates are on a downward trend, but vehicle prices are not expected to trend downward much with them. The tax incentives for electric vehicles (EVs) in the Inflation Reduction Act buoyed EV affordability for a narrow field of North American-made, qualifying vehicles, but they may get wiped out in the new year.
“2025 brings with it mixed opportunities and uncertainty for the auto industry as a new administration and policy proposals take hold,” says Chris Hopson, manager of North American light vehicle sales forecasting for automotive intelligence research firm S&P Global Mobility.
The only certainty is what trails in the rear-view mirror. Warnings of a demand-destroying recession over the last 2 yr. never came to fruition, and U.S. and global light-vehicle sales grew at a slow but steady pace, with EVs surpassing projections and the 1-million-unit mark in the United States.
Jonathan Smoke, chief economist for Cox Automotive, calls 2024 “one of the most normal years of car buying in a long time. Normalization dominates several trends especially in the used-car market and [2024] is looking to be the best year for consumers since the pandemic.” Many of his predictions held true:
- “Slow growth, but better than a recession; … it looks like we’ll get 2.7%.”
- “Consumers winning with vehicle-supply increases. As we entered 2024, new supply was back to spring 2020 levels.”
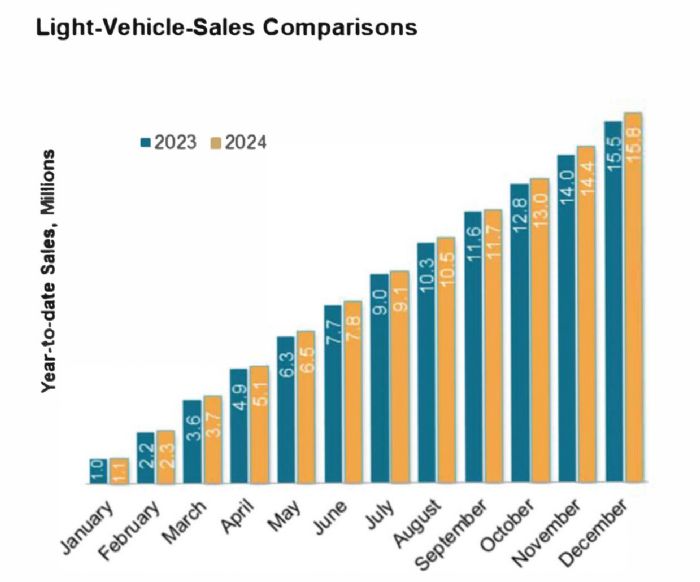
 North America sales volumes, per S&P Global Mobility, will climb to 16.18 million units in 2025, an increase of 1.2% from the 2024 level of nearly 16 million units, which was an increase of 3.25% over 2023 sales of 15.5 million units.
North America sales volumes, per S&P Global Mobility, will climb to 16.18 million units in 2025, an increase of 1.2% from the 2024 level of nearly 16 million units, which was an increase of 3.25% over 2023 sales of 15.5 million units.
Global sales in 2025 are forecast to increase by 2.37% in 2025 to 90.44 million units, up from 88.05 million units at the close of 2024, according to S&P Global Mobility. Business-advisory firm Riveron puts that number slightly higher at 91.9 million units. China continues to be the largest vehicle consumer in 2025, at a trajectory to buy 27.5 million units; North America next, at 19.6 million units, and Western Europe at 13.6 million units.
Pricing, inventory and affordability: Vehicle affordability remains one of the industry’s biggest challenges, but is expected to improve in 2025, according to Smoke. Credit availability also should continue to expand as loan-portfolio performance improves and yield spreads narrow. How much the Federal Reserve Board will cut interest rates is uncertain, but cuts will come, easing borrowing. “As we head into 2025, average auto-loan rates are a full point lower from their peaks earlier in 2024,” Smoke reports. “New-vehicle inventory volumes will continue on an upward trend in 2025, which will keep incentives growing, and manufacturers will be incentivized to move metal ahead of any policy shifts. Wage growth also is expected to continue as unemployment levels stay in check, another tailwind for sales.
“Yes, new vehicles remain expensive—suggested retail prices have jumped by nearly 25% in the past 5 yr.,” Smoke maintains. “But with sales incentives trending higher, auto-loan rates trending lower, and household wages growing, affordability has been improving for a year now, and more improvement is likely in 2025. That is good news for the market and the year ahead.”
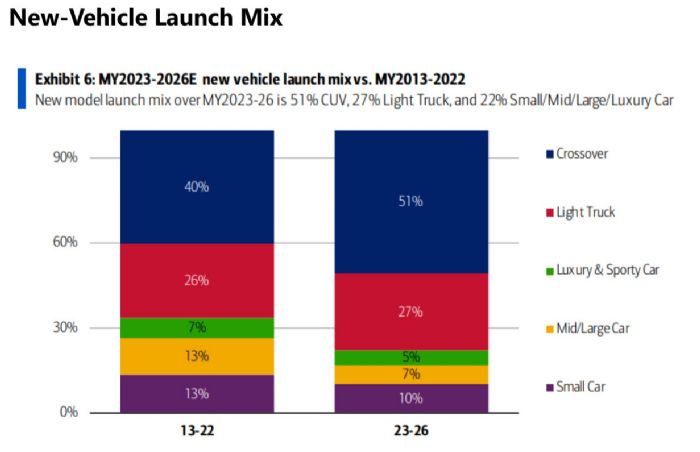
Mix: Crossovers and light trucks continue to dominate the mix, comprising almost 80% of current new models/launches. Riveron sees no reason for that trajectory to change.
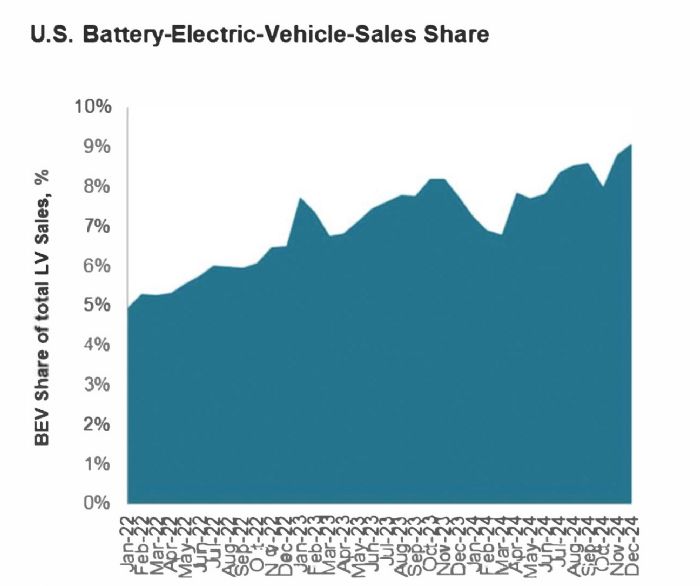
EVs: Smoke projects that one in four vehicles sold in the United States will be electrified—including hybrids and plug-ins—bringing them into the mainstream in 2025. “We remain firm in our continued belief that EV sales in the United States will follow a long-term growth path,” he says. “This past year, EV sales gains have been driven by brands not named Tesla, as the market leader saw lower volume year over year in 2024 and now accounts for less than half of the EV market.”
A record-breaking 1.3 million battery electric vehicles were sold in the United States in 2024, comprising 8% of the total market share of nearly 16 million vehicles sold across powertrain types. EV sales also jumped in Q4 to 356,000 vehicles, marking a 12% jump year over year. Some speculate that the fishtail spending was in reaction to the prospect that the Trump administration will carry out its threats to end the federal EV tax incentives in 2025—though only Congress has that power.
“Changes to the EV tax credits also are expected, although most shifts in policies will take some time to enact and ultimately be felt in the market, so the near term will be a continuation of the current positive trends, while worries about policy changes create urgency to buy now,” Smoke maintains.
“As we develop our forecast for 2025, we are mostly optimistic, as the market is finishing 2024 with momentum,” he concludes.—KB
Appliance Industry: Growth Continues
Forecasters expect continued growth in the home-appliance market, building on the previous 2 yr. of expansion but tempered by softer consumer demand and buying power.
The U.S. major household appliances market—refrigerators, freezers, dishwashers, ranges, microwaves, and washers and dryers—is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.15% through 2029, having reached $61.68 billion in sales in 2024, according to Statistica. The Farnsworth Group holds a more optimistic view, projecting 4.4% CAGR between 2025 and 2028, based on pent-up demand post-COVID and a return to supply-chain and pricing normalcy. As per the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistic’s Producer Price Index for Major Household Appliance Manufacturing, the huge price spike in mid-2021 to mid-2022 began leveling off through the end of 2022.
The large white-goods appliance segment showed the highest growth, from $775.31 million in 2023 to $824.79 million in 2024—a 6.6% rate of growth. It is expected to continue growing at a CAGR of 7.87%, reaching $1.31 billion by 2030, according to Research and Markets.
Statistica forecasts global market growth at a slightly higher CAGR, 4.87%, than stateside. The global household appliances market was valued at $490,452.88 million in 2023, is projected to reach approximately $983,193.41 million by 2035, and to grow at a CAGR of 6.03% through 2035.
Rapid urbanization in the major Asian Pacific economies is significantly driving the demand for kitchen appliances globally, according to Research and Markets. “A notable surge in the urban population is driving market growth for kitchen appliances in the next 5 yr.” While in major economies, such as the United States, where 83% of the country already is urbanized, in China, urban population stood at 64% in 2024.
Manufacturers may find it useful to note customer behavior and preference trends driving growth and how they may impact the market over the next few years:
- Smart home appliances. Manufacturers will see greater demand for components for smart appliances, as the worldwide household-appliances market is experiencing a surge in demand for these devices. Smart appliances have become more integrated and their usefulness more apparent, such as refrigerators that alert the homeowner to a door left open; a washing machine that notifies their smart phone when a cycle completes; or ovens that turn off when food is ready. In the United States, about 40% of homes have at least one smart appliance. The smart-home market is projected to grow by about 10% from 2025 to 2028, according to research from Oblero.
- Energy efficiency, sustainability. Energy prices continue rising, and major household appliances have a significant impact on a residence’s energy consumption. Consequently, appliance consumers increasingly are showing preferences for energy-efficient appliances in their new or replacement purchases, which may lead to higher demand for stamped electric and electronic components.
- Shrinking brand loyalty. Metal formers and stampers may receive RFQs from alternative customers, as consumers show increasing willingness to select a non-familiar brand. Samsung, LG, General Electric and Whirlpool remain the largest producers, but customers may become more motivated by cost and availability for major home appliances than by brand loyalty.
- Regional demand. Rising demand for large household appliances likely will draw from the growing housing sector in the southeast United States, according to Grand View Research.
- Online sales. Whether appliances are sold in a physical store or online may have little or no consequences for metal stampers and fabricators, but the online/in-store mix may alter packaging and transport. According to Statistica, U.S. online sales are expected to have totaled 56.7% of the revenue in the household appliances market in 2024, and 29.6% globally. However, The Home Improvement Research Institute cites 33% of sales being online and online/pick up sales in the United States, with two-thirds of sales occurring at a physical store, and home centers being the preferred retailer type.—KB
Big Boost for Aerospace Despite Supply-Chain Issues
 Forecasts are bullish on the aerospace market, currently valued globally at $328 billion and projected to reach $430.9 billion by the end of 2025, with a CAGR of 7%, according to the Redline Group.
Forecasts are bullish on the aerospace market, currently valued globally at $328 billion and projected to reach $430.9 billion by the end of 2025, with a CAGR of 7%, according to the Redline Group.
“Looking ahead, analysts predict exponential growth, with some estimates suggesting that the market could reach $1.2 trillion by the 2030s,” reads the group’s most recent report. “While forecasts vary, the consensus is clear: The aerospace industry is set for unprecedented expansion in the coming decade.”
We may see more than 45,000 new passenger, freighter and turboprop aircraft delivered between 2024 and 2043, according to Cirium’s Fleet Forecast, which also reveals that the number of active aircraft globally now exceeds pre-pandemic levels. Delivering an estimated 84% of aircraft, Airbus and Boeing are expected to remain the two largest commercial OEMs, with that percentage rising to 90% in value by 2043, according to Cirium. The Fleet Forecast predicts Asia as the continuing leading region in aircraft growth, responsible for 45% of deliveries over the next two decades, with China contributing 20%—nearly the North American total.
Per Deloitte, aerospace expectations remain lofty over the coming decade, especially considering that commercial-aircraft passenger volumes and revenues may have reached record highs in 2024, depending on yet-unavailable final year-end numbers. Deloitte, in its 2025 Aerospace and Defense Industry Outlook, does throw out supply-chain challenges as a major issue. Cirium backs this assessment, with its short-term forecast to 2027 predicting a 5% drop in deliveries due to supply-chain issues.
“Aircraft manufacturers are facing parts shortages in their supply chains, resulting in a shift in their scaling targets,” Deloitte’s report reads. “For instance, one major aircraft manufacturer’s supply chain is made up of nine layers, that contribute nearly 80% of the final jet components. Parts shortages and delivery delays are likely driven by global labor shortages and in-creasing geopolitical tensions.”
In fact, “an average U.S. commercial aerospace OEM has more than 200 Tier One suppliers and 12,000 Tier Two or Tier Three suppliers,” according to the Deloitte report. “These supply chains remained mostly resilient over the past few years. However, major industry players are currently confronting new supply-chain challenges including everything from securing their most critical materials to ensuring part and component deliveries. While many companies have begun working to balance supply-chain resilience with efficiency, parts shortages and delivery delays, shipping costs, and sourcing concerns are likely to continue impacting the industry, putting supply-chain visibility at the forefront.
“In 2025,” the report adds, “this may entail more companies employing digital technologies to track the flow of materials from upstream suppliers (for example, Tier Two and Tier Three suppliers) to end users and help oversee supplier compliance.”
Trends affecting the commercial-aircraft market include demand for fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly aircraft as Boeing and Airbus have adapted existing designs to improve efficiency and passenger comfort, according to Plunkett Research. Achievements include introduction of advanced engines and development of sustainable propulsion technologies such as hydrogen and electric power.
Other aerospace subsets besides commercial aircraft are expected to grow significantly in coming years. For example, we may see global delivery of as many as 8500 new business aircraft over the next decade to the tune of $280 billion, according to a Honeywell business-aviation outlook.
Specific to military aircraft, figures cited by Aviation Week include projections of more than $1 trillion in delivery value through the next decade, thus generating MRO demand of $1.4 trillion. Lockheed Martin is expected to lead the pack in military-aircraft manufacturing during this period, followed by Boeing.
And in the space segment, Deloitte, citing Space Foundation figures, reports that the global space economy grew to $570 billion in 2023, a 7.4% year-over-year increase, driven primarily by the commercial sector. Growth is expected to continue at a significant rate.—LK
Modest Growth for Heavy Equipment
 Expect demand for heavy equipment—having slowed in 2024—to experience modest improvement moving forward. Forecasts for agricultural, construction and mining equipment predict steady, slow growth in 2025 and beyond.
Expect demand for heavy equipment—having slowed in 2024—to experience modest improvement moving forward. Forecasts for agricultural, construction and mining equipment predict steady, slow growth in 2025 and beyond.
The global agricultural-equipment market, valued at $179.9 billion in 2024 and estimated at $189.1 billion in 2025, is projected to grow to $281.5 billion by 2033 at a 5.1% CAGR, according to Agricultural Equipment Market, a 2024 report from Straits Research. Drivers include increased mechanization and a rising population leading to increased demand for agricultural products. Agricultural-equipment producers found themselves in the news over the past few months for less-than-ideal reasons. Currently, depressed agricultural-commodity prices worldwide have affected equipment producers, with many reporting decreased sales and production cutbacks in 2024.
The global heavy-construction-equipment market tracks closely with the agricultural-equipment market, with a value of $180.3 billion in 2023 and anticipated to reach $277.5 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 5%, according to VynZ Research. And, with a value of $83.7 billion in 2024, the global mining-equipment market is estimated to reach $136.3 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 5.2% in this period, according to Global Market Insights.—LK
Construction and Related Hardware: A Mixed Bag
A continuing decline in interest rates and inflation as well as more favorable material and product lead times lead to cautious optimism for those in construction and related hardware markets. Since the pandemic, these markets have had a rough go, but forecasters at the close of 2024 see a somewhat improved operating environment in 2025 and beyond.
On the residential side, Oxford Economics forecasts housing starts in 2025 to increase by 6.2%. This would follow declines of 8.4% in 2023 and 4.7% in 2024. Global residential construction output is projected to increase by an average of 3.4% annually through 2025, according to ResearchandMarkets.com, with the United States experiencing a similar growth rate.
As for other sectors, “This is the era of the megaproject (courtesy of a resurgence in U.S. industrial policymaking and programs such as the Inflation Reduction Act, the Chips and Science Act, and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act), and future prospects are quite positive for contractors who are able to participate in major public works,” says Anirban Basu, chair and CEO of Sage Policy Group, as reported by Pallet Enterprise. “Manufacturers are receiving billions of dollars in subsidies for large-scale infrastructure projects, computer chip and battery manufacturing plants, and data centers, many in support of technological transformation such as the growth of artificial intelligence.”
Optimism does not quite hold for multi-family construction, hotels and retrofits of existing office space, as banks seem reluctant to lend for these types of projects. And overall, the American Institute of Architects (AIA) projects a spending increase of just north of 1% on nonresidential buildings in 2025, after a 7% gain in 2024. Worldwide, GlobalData forecasts 3% growth in global construction output for 2025, with the commercial sector contributing significantly to this expansion, and U.S. commercial-construction growth at a slower pace. AIA’s forecast also sees slow-paced growth in U.S. overall construction growth during 2025.
Strong fundamentals defined the overall U.S. construction industry in 2024, according to a Deloitte 2024 construction-outlook report, as spending surpassed $2 trillion in the first half of the year and employment—long an issue in the industry—rebounded to its highest levels since 2006. Even so, the construction industry averaged 382,000 job openings per month from August 2023 to July 2024, the industry had an average of 382,000 job openings each month—the third consecutive year with averages close to 400,000, Deloitte reports. The dearth of workers may impact project timelines. Consider, as Deloitte offers, that construction of a large data center typically creates nearly 1700 local construction jobs over a period of 18 to 24 mo. Staffing such projects may prove difficult in the near term.—LK
Huge Uptick in Electronics, Electrical Equipment
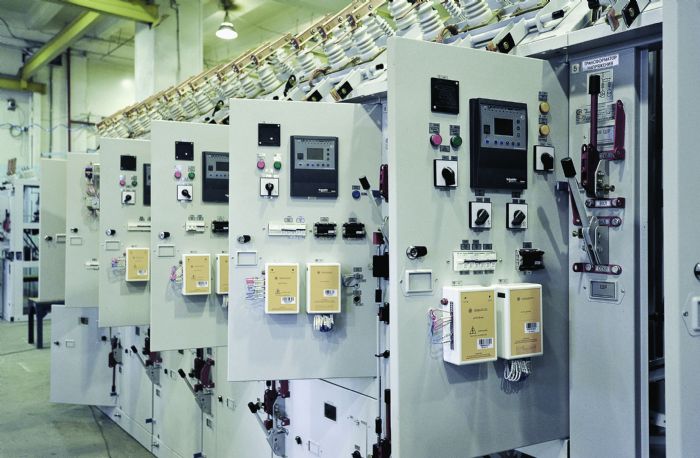 The electrical-equipment and electronics markets cut a wide swath in terms of opportunities for suppliers of sheet metal parts and components, from tiny pins and connectors to large panels and enclosures. A rising population, global concerns over energy consumption and sustainability, and the influx of Industry 4.0 technologies all push development and supply of advanced electrical and computer technology, leading to robust growth predictions for these markets.
The electrical-equipment and electronics markets cut a wide swath in terms of opportunities for suppliers of sheet metal parts and components, from tiny pins and connectors to large panels and enclosures. A rising population, global concerns over energy consumption and sustainability, and the influx of Industry 4.0 technologies all push development and supply of advanced electrical and computer technology, leading to robust growth predictions for these markets.
For instance, the global electrical-equipment market experienced a 4.33% CAGR from 2020 to 2023, and finished that period valued at $1.54 trillion. It is expected to reach $2.17 trillion by 2030, according to ResearchAndMarkets.com.
“In the industrial sector, energy-efficient motors, transformers and electrical machinery are in high demand as manufacturers seek to improve productivity while minimizing energy consumption,” reads a 2024 report from ResearchandMarkets.com. “Advanced motor-control systems, such as variable-frequency drives, optimize the performance of electrical motors … and similarly, energy-efficient lighting systems, such as LEDs, are increasingly being adopted across residential, commercial and industrial sectors. The sustainability trend also is driving demand for electrical equipment designed to support green buildings, smart grids and renewable-energy systems.”
Also, the emerging trend of transportation-sector electrification significantly drives demand for electrical equipment.
“This transition requires extensive electrical infrastructure, including charging stations, grid upgrades and energy-storage systems,” the report from ResearchandMarkets.com states. “The growing adoption of electric vehicles has led to a surge in demand for charging infrastructure, which depends on electrical equipment such as transformers, power converters and metering systems.”
A driver of the electronics market, worldwide IT spending is expected to total $5.74 trillion in 2025, a 9.3% increase from 2024, according to the latest forecast by Gartner, Inc. Note, too, that the global consumer-electronics market, valued at 1.07 trillion in 2022, is projected by Grand View Research to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% through 2030.
Next-generation computer memory, found in all manner of products and a leading indicator for electronics-market overall health, is soaring. Valued at $1.15 billion in 2023, the global market for next-generation memory is expected to achieve a CAGR of 22.6% through 2030 and a valuation of $4.88 billion, according to Valuates’ 2024 Next Generation Memory Market report.
AI applications also drive the need for next-generation memory, with their demands for rapid data processing and large memory storage. And, “edge computing, which processes data closer to its source, requires quick and reliable memory to ensure real-time processing,” the Valuates report offers. “Next-generation memory solutions are crucial in this regard, as they offer the speed and durability needed to support edge-computing applications. High-bandwidth memory solutions are essential for data-intensive applications such as 3D rendering and data analytics. Next-generation memory provides the necessary bandwidth to handle these applications efficiently, positioning them as valuable assets across various industries.”
More good news for suppliers in the electronics space: spending on data-center systems increased nearly 35% in 2024, and is expected to grow in 2025 as well, according to Gartner. Server sales provide the largest push in this area, “set to nearly triple from more than $134 billion in 2023 to $332 billion by 2028, including more than $257 billion in 2025,” reads the Gartner forecast.—LK
A Steady HVAC Market
 Per data released in December by the Air Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute, collected in October 2024, year-to-date (YtD) U.S. shipments of residential gas storage water heaters had dropped by 2.2% compared to shipments during the same period in 2023. Shipments of residential electric storage water heaters had risen by 5.4% YtD compared to 2023. Likewise, shipments of commercial gas storage water heaters dropped by 3.6% year-over-year, but shipments of commercial electric storage water heaters rose by 5.8%.
Per data released in December by the Air Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute, collected in October 2024, year-to-date (YtD) U.S. shipments of residential gas storage water heaters had dropped by 2.2% compared to shipments during the same period in 2023. Shipments of residential electric storage water heaters had risen by 5.4% YtD compared to 2023. Likewise, shipments of commercial gas storage water heaters dropped by 3.6% year-over-year, but shipments of commercial electric storage water heaters rose by 5.8%.
Meanwhile, the market for furnaces grew marginally in 2024. YtD U.S. shipments (as of October 2024) of gas warm-air furnaces grew by 2.5% compared to 2023. And YtD shipments of oil warm-air furnaces grew by a whopping 39.9%.
Finally, YtD combined shipments of central air conditioners and air-source heat pumps grew by an impressive 8.9% through October 2024, compared to the same period in 2023. Sales of central air conditioners rose by 7.1% in 2024, and heat-pump sales climbed by 11.4%.
The HVAC industry finds itself at the center of the public-policy discussions surrounding energy use and the environment. Those concerns, including the transition from hydrofluorocarbons to low-GWP (global warming potential) refrigerants, will impact the supply chain. For example, the use of GWP refrigerants potentially requires different types of metal alloys used in fabrication, and design modifications to heat exchangers and other system components. Too, many low-GWP refrigerants are flammable, so fabricated components might require upgraded leak-detection systems.
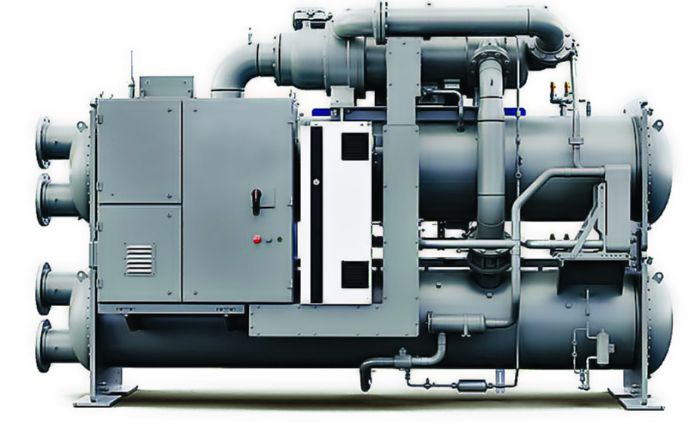
As an example, in March 2024 Carrier Corp. introduced a single-state heat pump that reportedly is the first available in the field compatible with the low-GWP refrigerant R-454B. And, in July 2024 the firm introduced the availability of its AquaEdge 19MV water-cooled centrifugal chiller compatible with ultra-low GWP refrigerant R-1234ze(E). Carrier manufactures the chiller at its factory in Charlotte, NC.
Market-research firm Technavio forecasts the global HVAC market to grow by a CAGR of 6.55% from 2024 to 2028, driven by increased infrastructure development, growing demand for cooling units, an increase in urban population, and increased construction of residential buildings. Technology advancements also drive demand—integration of smart technologies, artificial intelligence and machine learning, for example.
In the United States, industry revenue has grown at a CAGR of 0.7% over the past 5 yr., according to IBISWorld. In North America, Fortune Business Insights projects the HVAC market to expand by a CAGR of 5.4% through 2030. And, in a report from SunZero titled 2025 Trends in Heat Pumps and HVAC: What Residential Consumers Need to Know, we learn:
- The pressure to reduce carbon emissions is driving significant changes in HVAC systems. Heat pumps, which use electricity to transfer heat rather than generate it, are seen as a key technology in decarbonizing homes. By 2025, heat pumps will become even more efficient, with advances in technology enabling them to operate effectively in colder climates.
- The synergy between heat pumps and renewable-energy sources such as solar panels is a trend that will continue to grow in 2025. By pairing heat pumps with solar photovoltaic systems, homes can be heated, cooled and powered using clean energy generated onsite.
- The rise of smart-home technology is having a significant impact on the HVAC industry. By 2025, we can expect to see heat pumps and other HVAC systems becoming smarter, more connected and more integrated with home automation platforms. Smart HVAC systems will go far beyond simple remote control. Advanced sensors and machine-learning algorithms will enable these systems to learn from user behavior, predict heating and cooling needs, and adjust settings automatically for optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
- With more people working from home and spending increased time indoors, flexibility in heating and cooling needs has become more important. Enter modular HVAC systems, which can be customized to fit the specific needs of different parts of the home. Ductless mini-split systems are a great example of this.—BK
Medical-Device Market on a Rapid Rise
 The contract medical-device manufacturing market, valued at $88.8 billion in 2022 per Coherent Marketing Insights, is projected to more than double by the end of the decade, to $192.3 billion. Primary drivers include growing demand for minimally invasive surgical procedures and continued outsourcing by OEMs. For their part, contract manufacturers in this space have adopted emerging technologies, including advanced IIoT solutions and AM, to enhance productivity and quality, and to facilitate customized production in low volumes. By providing end-to-end services, from product design to regulatory approvals, their OEM customers can reduce production costs and time-to-market.
The contract medical-device manufacturing market, valued at $88.8 billion in 2022 per Coherent Marketing Insights, is projected to more than double by the end of the decade, to $192.3 billion. Primary drivers include growing demand for minimally invasive surgical procedures and continued outsourcing by OEMs. For their part, contract manufacturers in this space have adopted emerging technologies, including advanced IIoT solutions and AM, to enhance productivity and quality, and to facilitate customized production in low volumes. By providing end-to-end services, from product design to regulatory approvals, their OEM customers can reduce production costs and time-to-market.
In particular, miniature and disposable medical devices have gained prominence, and contract manufacturers have opportunities to manufacture devices for drug delivery, endoscopy and cardiac monitoring, among others. And, there is increased demand for customized devices tailored to individual patient needs and conditions. Here, AM has revolutionized the production of highly customized and complex components, including prosthetics and implants.
Also noteworthy: Surveys reveal that approximately 17.3% of the U.S. population is over 65 yr. old, and by 2030 that rises to 20%. Europe sees the same trend, as 28% of its population will be 65 and older by 2030. This trend, per Verified Market Research, will help to drive growth in the market for hospital equipment and supplies, predicted to grow by a CAGR of 12.21% from 2024 to 2031.
The equipment used in hospitals continues to evolve at breathtaking pace, evidenced by rapid adoption of AI-enabled medical devices. The FDA, for example, reported early in 2024 a 55% increase in AI-integrated diagnostic-device approvals.
Finally, medical-device OEMs are committed to moving their supply chains toward carbon neutrality, asking suppliers to use sustainable materials and processes to reduce environmental impact. The goal: Move toward a circular healthcare economy that’s driving the development of durable and reusable products and materials. As an example, early in 2024 the Healthcare Climate Council reported a 30% increase in hospitals adopting green medical equipment.—BK MF
View Glossary of Metalforming Terms
Technologies: Management









 Metal formers also forecast an increase in incoming orders, with 34% of survey respondents forecasting an increase in orders during the next three months, compared to 30% in November, and just 19% anticipating a decrease in orders, down from 30% in November.
Metal formers also forecast an increase in incoming orders, with 34% of survey respondents forecasting an increase in orders during the next three months, compared to 30% in November, and just 19% anticipating a decrease in orders, down from 30% in November.
