While shipping logjams and prices recede, inflation and raw-material concerns continue. Inflation seems to have slowed, and geopolitics—i.e., Russia-Ukraine war, China-Taiwan issues—will bear close watching in 2023. Uncertainty in regions depended upon for various alloys and other materials may well affect markets, including EV development in automotive.
Overall in the United States, expect economic improvement to continue in 2023 across manufacturing and service industries, according to purchasing and supply-management executives polled in the Institute for Supply Management December 2022 Semiannual Economic Forecast. Revenues are expected to increase in 15 of 18 manufacturing industries with capital expenditures expected to increase by 2.6 percent after a 12-percent increase in 2022. The manufacturing employment base is expected to grow by 3.9 percent in 2023.
Let’s take a closer look into 2023 and beyond for markets near and dear to the metal forming and fabricating communities.
Automotive
No industry has been hit harder by supply-chain woes and computer-chip shortages than automotive manufacturing. Fortunately, we’re reaching the light at the end of the tunnel, and within that light we see more uncertainty as to how the major focus on EVs will play out over the next decade.
LMC Automotive in January 2023 reports U.S. light-vehicle sales of 13.7 million in 2022, the lowest total since 2011, despite a year-over-year increase of 7.2 percent in December 2022. As for the near term, S&P Global Mobility predicts global new light-vehicle sales to reach nearly 83.6 million units in 2023, a 5.6-percent increase year-over-year. This follows projections for full-year 2022 light-vehicle sales to reach nearly 79.2 million units, representing a 1.3-percent decline from 2021 levels.
 “The auto industry continues to navigate supply-chain challenges while confronted by several markets facing deteriorating economic conditions and fading pent-up demand,” the forecast notes. “As semiconductor availability plays out, demand destruction is expected to take a more fundamental role in 2023, impacting production and the inventory restocking cycle.”
“The auto industry continues to navigate supply-chain challenges while confronted by several markets facing deteriorating economic conditions and fading pent-up demand,” the forecast notes. “As semiconductor availability plays out, demand destruction is expected to take a more fundamental role in 2023, impacting production and the inventory restocking cycle.”
By region, Western/Central European 2022 vehicle sales should post 12.9 million units, a 6.7-percent decline year over year, and 2023 demand is forecasted at 13.9 million. U.S. sales volumes are expected to reach 14.8 million units in 2023, an estimated increase of 7.0 percent from the projected 2022 level of 13.8 million units. And for mainland China, S&P Global Mobility analysts report 2022 sales will end up at 24.8 million units, up 3.6 percent year over year, and project 2023 sales of 25.9 million units.
Economic health will have quite a say in light-vehicle sales. While the risk of recession in 2023 remains, Cox Automotive expects the economy to experience slowing or very weak growth as the Federal Reserve tightens monetary conditions and consumers continue to wrestle with high interest rates.
“A job-wrecking recession is a worst-case scenario for the auto industry, but hope for an economic soft landing remains,” a 2023-prediciton piece from Cox Automotive reads. “Either way, a sputtering economy will hold back the auto market in the year ahead. (And,) new-vehicle production challenges are beginning to ebb, and inventory levels are measurably improving. While lingering supply-chain and labor challenges will remain, and capacity will not return completely to pre-pandemic levels in the foreseeable future, stronger production levels and softer demand will lead to higher days’ supply and, ultimately, more vehicle options for shoppers in 2023.”
Within the overall light-vehicle market, U.S. EV sales will surpass 1 million units in 2023, according to Cox Automotive, as the automotive industry backs up its all-in mindset. How all-in?
“While EVs only accounted for 8 percent of global sales in 2021, production and market share are set to explode to an estimated 33 percent of global sales by 2028, and as high as 54 percent in 2035,” as cited in a report from USC Consulting Group. “Not only that, but the total EV investment among automotive suppliers and manufacturers is set to reach $526 billion between 2022 and 2026, nearly double the investment from the beginning of the decade.”
And, by 2029, predicts AutoForecast Solutions, EVs may represent one-third of the North American market and 26 percent of vehicles produced worldwide.
A late-2022 OESA event featuring an automotive tooling update from Harbour Results, Inc. (HRI) dove deep into economic factors affecting future automotive production, and how the industry will cope with automotive electrification. Overall, Covid, supply-chain issues and especially chip shortages resulted in 8 million light vehicles completely disappearing from production since 2021, Joe McCabe, president and CEO of AFS told the assembled. The high-water mark of North American light-vehicle production, 17.8 million, will not be reached again, he forecasts, until much later this decade, possibly as late as 2029.
As for the EV hype, “Wall Street loves tech,” Laurie Harbour, HRI president and CEO told attendees. “You see it in investments in batteries, EVs…companies are setting electrification goals in order to boost stock prices. With this as the end goal, OEMs are all-in on electrification.”
For suppliers of tooling, “we’ve already been through the slowdown,” Harbour said, noting that tooling spend reflects future expectations, thus suppliers have weathered the worst of the automotive downturn.
In fact, recent automaker profits are funding an increased number of new-vehicle launches over the next few years, which will lead to a year-over-year 13.4-percent increase in North American automotive-vendor tooling spend, according to HRI in its most recent Harbour IQ report.
Several key factors are driving the increase in tooling spend, the report notes. First, despite a drop in North American vehicle demand, most automakers are experiencing record levels of profit per vehicle sold. This strong performance is funding investment in technology and new vehicles. From 2023-2029 the number of vehicle nameplates in the region will grow 18 percent—from 210 to 249. Additionally, EV nameplates will grow from 20 percent of the mix in 2023 to 46 percent in 2029. New nameplates generate new launches, which require more tools. Further, the Detroit Three automakers, who source most of their tools in this region, plan to source tooling for new full-sized pickup trucks and SUVs in 2024, 2025 and 2026, which significantly increases tooling demand. The Harbour IQ study shows that the discrete number of tools will increase by 14 percent CAGR from 2022 to 2025, driving more demand for tooling with all of the new models.
“Despite economic uncertainty and supply-chain challenges, we see a bright future for the automotive tooling industry,” offers Harbour. “Although we see growth within the industry, it is important to note that North American tooling spend per vehicle for BEVs on average are lower than ICE vehicles by about 30 percent. Although we see tooling spend and the number of tools sourced increasing over the next few years, the average spend per tool will decrease. So, it will be important for mold and die companies to focus on improved efficiency and throughput.”
Aerospace and Defense
Navigating uncertain times in these two sectors requires a close eye to five trends, as described in Deloitte’s 2023 Aerospace and Defense Industry Outlook:
1. Supply chain
“Focus on supply-chain visibility and resilience to mitigate a broader set of risks,” the report reads.
2. Digital transformation
“Acceleration of digital thread and smart factory can drive improved efficiencies.”
3. Talent
“Attracting, retaining and developing top talent remains a challenge.”
4. Decarbonization
“Lowering emissions and implementing sustainable manufacturing remain business priorities.”
5. Emerging markets
“Innovation accelerates growth in emerging areas. Business agility and digital transformation will be key to staying ahead.”
While the aerospace and defense industries exhibited signs of a strong rebound in 2022, supply-chain and labor-force issues limit growth, according to Deloitte’s outlook, and the Russian invasion of Ukraine disrupted global supply chains and exacerbated fuel-price volatility. Other forces at play include demand for passenger travel, which directly relates to ticket prices and rises and falls with the price of fuel.
All of this has aircraft manufacturers investing in more fuel-efficient aircraft and engine designs to lower operating costs, and exploring lower- and zero-emissions commercial aircraft.
“The strong recovery in air travel is leading to increased aircraft orders and aftermarket activity,” notes the study. “Domestic traffic levels (in September 2022) registered about 81 percent of the pre-pandemic 2019 levels and international traffic levels have shown strong growth with easing travel restrictions worldwide.”
Adding to this, OEMs, the study finds, predict that by the end of 2023 or early 2024 global passenger traffic will return to 2019 levels. Look for increased travel abroad by U.S. residents, in particular, as 31 percent of Americans (per a poll by tourism-market research firm Destination Analysts) are more interested in international than domestic travel.
On the commercial-aircraft side, the global commercial aviation market is projected to register a CAGR of 7.65 percent, according to Mordor Intelligence. Commercial aircraft orders during the third quarter of 2022 were at their highest since 2015, notes a Simple Flying report, with a total of 670 planes ordered. “While more than 600 of the aircraft ordered are narrowbodies, Q3 also saw a rise in demand for widebody jets,” the report reads.
Among recent industry news: Airbus projects that over the next 20 years it will deliver more than 38,000 new airplanes; and late in 2022 United Airlines agreed to purchase at least 200 Boeing planes, split between two models—the 737 Max and the 787 Dreamliner. Similarly, Delta Airlines ordered 100 Boeing 737 Max aircraft during Q3 2022.
Regarding the defense industry, the Deloitte report notes that the segment remained “stable through 2022 and is expected to outperform the commercial aerospace segment as an increase in defense budgets in the wake of the invasion is boosting demand for military equipment globally.”
In addition, the FY 2023 U.S. defense budget aims to address strategic threats from China and Russia, with moneys allocated to developing electronic warfare and cybersecurity.
The majority (88 percent) of Deloitte’s survey takers say that they believe the general business outlook for the aerospace and defense industry for the coming year is “somewhat to very positive.”
“Companies focused on innovation and (that are) prepared to capitalize on new emerging opportunities could outperform their peers in 2023,” the study concludes.
Drilling down, diversifying the supplier base for critical supplies is a top priority to build and manage supply-chain resiliency. Leading primes have shown meaningful progress in reducing Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions in 2022, yet “they face challenges in tracking emissions across operations and the value chain,” the study notes. “According to the International Data Corp., 80 percent of global manufacturers will incorporate environmental sustainability in their products by 2024.”
Further, a report from Data Bridge Market Research predicts that the global aerospace parts-manufacturing market will witness “significant growth during the forecast period (2022-2030) due to increasing demand for lighter, innovative and efficient airplanes to reduce carbon emissions.”
Appliance
Revenue in the U.S. major appliance market (dishwashing machines, refrigerators, cookers and ovens, freezers, and washing machines) is expected to grow by a 2.56-percent CAGR through 2027; the segment is expected to show a volume growth of 3.2 percent in 2023. This according to Statistica.
Helping to drive sales: rapid adoption of IOT technology within smart household appliances. As noted in a ResearchandMarkets report:
 “Due to busy schedules and lack of time to manage daily routine activities, an increasing number of people in the United States are preferring residence with advanced facilities such as dishwashers, grinders, coffee makers, etc., to save time. Further, the market is expected to increase due to a growing number of single-person households, surging urban population, growth in number of smart homes, rising millennial population, improved and surging online sales of small household appliances, surging demand for smart sensors, and rising demand for energy optimization.”
“Due to busy schedules and lack of time to manage daily routine activities, an increasing number of people in the United States are preferring residence with advanced facilities such as dishwashers, grinders, coffee makers, etc., to save time. Further, the market is expected to increase due to a growing number of single-person households, surging urban population, growth in number of smart homes, rising millennial population, improved and surging online sales of small household appliances, surging demand for smart sensors, and rising demand for energy optimization.”
Suppliers not only seek to deliver innovation such as connectivity and enhanced user experiences, but also to be sensitive to the environment, including investing in the use of sustainable materials, increasing energy efficiency in products, and responsible recycling, as well as providing refurbished and repairable devices, while lowering their carbon footprint. Think clothes dryers equipped with sensors and algorithms to measure the moisture content of clothes, and then able to adjust drying time and temperature to optimize drying cycles; washing machines that automatically identify fabric types and dirt levels, optimizing performance; and mobile apps consumers can use to remotely monitor and control appliances.
ESG (environmental, social and governance) is top of mind throughout the industry, exemplified by Whirlpool announcing, in September 2022, its plans to source sufficient renewable energy for 100 percent of electricity for its U.S. plant operations. Whirlpool previously had announced its 2030 commitment to net-zero goals, pledging to reach net zero across more than 30 global manufacturing sites and distribution centers. Initiatives outlined by Whirlpool to attain these goals include working toward 100-percent renewable-energy usage through wind and solar-panel installations, and power purchase agreements that fund wind and solar farms, as well as energy-efficiency programs at the company’s plants and facilities, and offsets for remaining emissions that can’t be avoided.
Along similar lines, Electrolux, in recognizing its top global suppliers in November 2022, says that it looks for suppliers that value “operational excellence, sustainability and innovation, which are key to delivering outstanding branded lifetime experiences for our consumers,” according to chief purchasing officer Filippo Milanese.
And not to be outdone, GE opened a new micro factory in 2022, in Stamford, CT, and then, in October, announced plans to invest $1 billion cumulatively with diverse-owned suppliers by 2030. Says Kevin Nolan, president & CEO of GE Appliances: “We made this commitment because a diverse and resilient supply chain here in America is critical to our success—it’s the right thing to do, it’s good for our business and it’s good for the communities that we serve.”
All of that said, manufacturers have felt the economic pinch of inflation. A mid-2022 press release from Electrolux notes weaker-than-expected consumer demand in Europe and North America, driving the company to cut costs in both regions and to launch a turnaround program in North America. “High inventory levels at retailers and production inefficiencies and high costs caused by continuing supply-chain problems are adding to these challenges,” according to the release.
Whirlpool had noted similar mid-year challenges, reporting a net sales decline of 4.3 percent caused by disruptions in the supply chain and a slowdown in demand.
Construction/Off-Highway
One year after its inception, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) is “poised to advance the American clean-energy transition and the Biden administration has taken many steps to operationalize the provisions,” notes a late-2022 Power Line article from American Clean Power. Touted as the largest-ever investment in clean-energy infrastructure (until passage of the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022), the IIJA “set us on a path to make unprecedented investments to modernize and enhance the nation’s electrical grid,” the article points out.
Paired with the Inflation Reduction Act, the IIJA provides the policy foundation on which the clean-energy industry began to build a new energy-transmission infrastructure. Most recently, in November 2022, the U.S. Department of Energy (DoE) issued its first funding announcements for the Transmission Facilitation Program and more than $3 billion in grant funding for the Grid Resiliency and Innovative Partnerships programs—with plans to begin issuing awards in 2023.
 Energy storage also has taken center stage, as IIJA earmarks significant funds for further investment in energy storage, including grants from the DoE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy for processing, manufacturing and recycling of battery materials, as well as grants and cooperative agreements from the DoE Office of Clean Energy Demonstration to carry out energy-storage demonstration projects.
Energy storage also has taken center stage, as IIJA earmarks significant funds for further investment in energy storage, including grants from the DoE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy for processing, manufacturing and recycling of battery materials, as well as grants and cooperative agreements from the DoE Office of Clean Energy Demonstration to carry out energy-storage demonstration projects.
“We’re sitting at 14- to 15-yr. highs in the Dodge Momentum Index,” says Richard Branch, chief economist for Dodge Data & Analytics, “so it should provide some semblance of confidence and reassurance that developers and owners are continuing to put projects into the queue despite the fact that we’re concerned about what might happen when interest rates keep rising and the economy slows down in 2023.”
The 2023 construction outlook by sector, per Dodge:
- Residential: Single-family housing starts down 6 percent in 2023. The market’s trough is predicted to hit in late Q1/early Q2 2023 as mortgage rates stabilize. Meanwhile, multi-family housing starts—coming off of their best year since 1986—are predicted to drop 9 percent in 2023.
- Nonresidential: Commercial starts are expected to drop 3 percent, Branch predicts, noting two poor performers: warehouses and office construction. Says Branch: “2022 was the peak year for warehouse construction. Bright spots for the segment include retail and hotels.
- Manufacturing plants: While starts will fall by 43 percent, this comes on the heels of 196-percent growth in 2022 as more companies opted to shift production back to the United States. “You need to go back to the early ’90s to see the kinds of square footage that we expect to break ground in 2023,” Branch says.
- Institutional sector: Government funding will provide stability for government, education and healthcare projects, especially in regions with strong demographic growth such as the Carolinas, Florida, Texas, Nevada and New Mexico.
- Environmental: Public-works starts are set to rise with work on dams/reservoirs up 15 percent; water-supply systems up 12 percent; and sewage and waste up 17 percent.
- Lastly, looking just at roads and bridges, only 19 percent of funds from the latest infrastructure package have been allocated so far. “There’s a lot of money still on the table waiting to be spent,” says Branch. “We continue to think that 2023 and 2024 are the best years for infrastructure construction.”
As for the off-highway market, a state-of-the-industry report from OEM Off-Highway echoes the common sentiment around manufacturing when it comes to identifying challenges, that is: Supply-chain challenges require manufacturers to invest in engineering and manufacturing experts to help navigate a complicated climate and localize supply chains to ensure the supply is close to customers.
The industry also continues to transition from diesel internal combustion engines to electric and alternative fuels (biofuels and hydrogen). And “most off-highway OEMs are adopting or have adopted the global environment, social and governance (ESG) goals,” the report notes.
Overall, the global market for offroad vehicles is predicted to grow by an 8-percent CAGR through 2032 (Global Market Insights). In particular, the recreational off-highway vehicles market is expected to grow at a 13.2-percent CAGR through 2032 (Fact.MR).
Among new technology entering the sector, an OEM Off-Highway article reviewing the 2022 Consumer Electronic Show highlights the new John Deere fully autonomous tractor, equipped with six pairs of stereo cameras to create 360-deg. obstacle detection; and the launch of the Bobcat T7X all-electric compact track loader equipped with an intelligent power-management system programmed to sense when loads are increasing, and then to automatically back off power when not needed to conserve energy and runtime.
Electronics
A stay-at-home mindset throughout the Covid pandemic helped drive electronics-industry gains, tempered by the computer-chip shortage. With the pandemic winding down and chip production rising, forecasters expect modest global growth in this sector for the near-term. Look for a CAGR of roughly 5 percent through 2024. Through 2027 according to analysts from ReportLinker, the electronics manufacturing services market is poised to grow by $167 billion, accelerating at a CAGR of 6 percent.
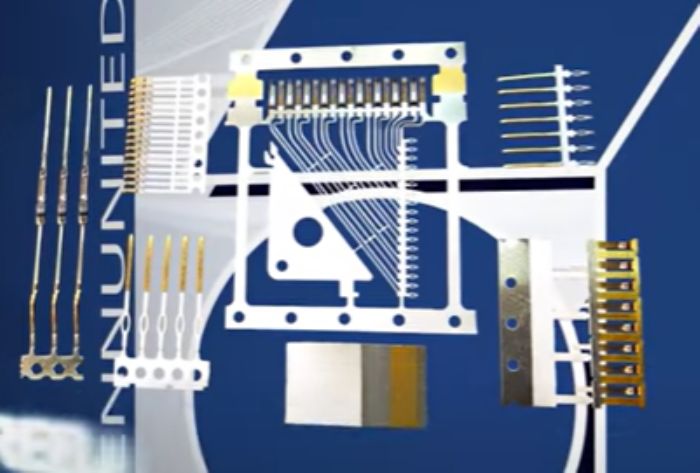 The downturn hitting components and semiconductors is likely to continue for at least the first half of next year, according to Michael Yang, analyst for Omdia.
The downturn hitting components and semiconductors is likely to continue for at least the first half of next year, according to Michael Yang, analyst for Omdia.
“We probably are not yet at the bottom,” he says, as quoted in Design News. “There will be an excess of supply and slowing demand for the next three to six months (through June 2023), until macroeconomic conditions work themselves through.”
While artificial intelligence and automotive continue to drive demand for electronic parts, Yang notes, consumer electronics, smartphones and data centers comprise the most applications for electronics parts.
The copper market represents a key indicator for the electronics-manufacturing market, with electronics driving an expected CAGR of 4.9 percent through 2030 to $447 billion, according to Acumen Research and Consulting (ARC). While ARC pegs the Asia-Pacific region as dominant in copper-market share—67 percent—we can expect the North American copper market to grow by a CAGR of 45.1 percent through 2030.
Assuming the expected full recovery of chip supplies, many remain bullish on this sector. Case in point: Penn United Technologies. Last fall the company opened its Advanced Materials Processing Facility in Sarver, PA, a 50,000-sq.-ft. facility housing a new electroplating line. The new line, as explained by company president and CEO Bill Jones, enables it to expand electroplating capacity by 20 percent for inhouse-stamped metal connectors and terminals.
“During the last few years,” says Jones, “we have experienced unprecedented demand driven by exponential growth in our connected world, and the need for stamped and plated electrical contacts and terminals. As a result, we have outgrown our current facility.”
HVAC
“The future of the U.S. heating, ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC) equipment market looks good, with opportunities in commercial and residential sectors,” notes a recent ReportLinker article. The U.S. HVAC-equipment market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 3.4 percent through 2027, with major market drivers including a higher rate of building renovation and federal tax credits to make existing facilities energy efficient and control greenhouse-gas emissions.
In another HVAC-market report, Grandview Research adds, “Global warming and the resultant extreme climatic conditions will help uptick market demand… In addition, the demand for energy-efficiency equipment together with the growing real-estate market also will (increase) HVAC demand.”
Noted trends directly impacting industry dynamics include green HVAC systems, nanotechnology in air-conditioning systems, and use of solar power for heating and cooling. Further, the U.S. government continues to offer rewards promoting low power consumption and the use of renewable-energy sources.
In addition, according to ReportLinker, “standards established by the U.S. government to keep a check on HVAC-system operations will play a pivotal role in driving demand. In addition to efficiency standards on the demand side, standardizing manufacturing processes on the supply side of the market also has helped tremendously in reducing hazards to the environment and carbon emissions… U.S. customers have access to favorable tax credit and rebate programs.”
On the supplier front, Lennox recently announced plans to explore “strategic alternatives for its European commercial HVAC and refrigeration businesses,” according to a recent press release, “which represent approximately 5 percent of the company's revenue,” said company CEO Alok Maskara. “This decision is consistent with our focus on North America, where we are best positioned to achieve our revenue growth and profit margin targets." In addition, the company pledges to continue to invest in its high-performing North American Heatcraft Refrigeration Products business. "With an even sharper focus on North America, Lennox has significant opportunities ahead to accelerate profitable growth over the coming years,” added Maskara.
Driving innovation in the sector are new federal regulations (effective January 1, 2023). According to a recent website article from industry supplier Carrier: “Every 6 yr. the Department of Energy (DoE) reviews the effects of energy usage, sets minimum efficiency requirements and manages the testing standards by which those efficiencies are measured. As a result of its most recent analysis, the DoE is increasing the minimum efficiencies for central air conditioners and heat pumps.”
Exemplifying the impact of the new regulations, Carrier in mid-2022 launched a new line of single-stage split-system air conditioners compliant with the upcoming DoE minimum-efficiency requirements and test procedures. The units feature patented welded-aluminum coils, along with decreases in height, base-pan size and weight.
Among other noteworthy enhancements made by HVAC suppliers: Trane’s debut of an all-aluminum spine-fin design for its variable-speed inverter heat pump, to enhance air flow and heat transfer compared to conventional copper and aluminum coils; and Lennox introduced a prototype cold-climate heat pump, designed to warm homes in the northern U.S., which employs a supersized compressor that uses vapor-injection technology.
Medical
“Delayed and cancelled elective surgeries, long lead times, significantly higher costs—this has been the unfortunate state of affairs,” reads a newly produced whitepaper, Looking Ahead: Risk Outlook for the Medical Supply Chain, from FTI Consulting. “Extensive and unprecedented supply-chain disruptions in the medical-device industry have materialized and sustained over the last 30 months, including raw-material shortages, labor challenges, sterilization constraints and concerns surrounding device security and cybersecurity.”
 For example, “Elective surgeries were and remain our bread and butter... we saw an 82 percent decline in sales during the pandemic,” the whitepaper quotes Howard Levy, vice president of global sourcing and instruments at Zimmer Biomet.
For example, “Elective surgeries were and remain our bread and butter... we saw an 82 percent decline in sales during the pandemic,” the whitepaper quotes Howard Levy, vice president of global sourcing and instruments at Zimmer Biomet.
Despite such challenges, the near-term future seems promising in the medical-manufacturing arena. The global medical-device manufacturing outsourcing market—led by North America—is estimated to grow by more than $46.2 million from 2022 to 2027 at a CAGR of 10.85 percent, according to a report from Technavio. Major trends in the market: a growing focus of OEMs on reducing medical-device manufacturing costs; growing complexities in product design and development; and emerging countries as a preferred outsourcing destination for medical-device manufacturing. Challenges listed by Technavio include a stringent regulatory environment, intense market competition, and delays in contractual obligations and the upgrading of technologies.
For years to come, expect the integration of smart connected care; broadening of diagnosis and therapy into new settings; and improvement of chronic disease outcomes to continue shaping the market, according to a 2023 outlook from In Vivo. Just as with other markets, medical must navigate supply-chain, inflation and workforce stresses.
Specific to medical-device manufacturing are issues revolving around sterilization procedures and materials, according to FTI Consulting. Many manufacturers involved in polymers rely on ethylene oxide (EtO), with EtO used to sterilize more than 50 percent of U.S. products made from polymers. However, regulators have EtO, designated as a human carcinogen, in their sights. Alternative sterilization methods include steam and dry heat, radiation, vaporized hydrogen peroxide and other gases.
The Russian-Ukrainian War, FTI Consulting reports, is testing supply of critical raw materials used in medical-device production, stemming from import restrictions, concentration of production in relatively few countries and decades of bilateral dependency.
We do see manufacturers investing to meet expected demand. For example, Okay Industries, a New Britain-CT a contract manufacturer of metal and plastic overmolded components and subassemblies for global medical-device OEMs, recently announced a major expansion of its Costa Rica operations. Phase one includes building a 62,000-sq.-ft. manufacturing facility in Alajuela Province, Grecia—to be completed by summer 2024. This will double the company’s current Costa Rica manufacturing footprint. Future phases will allow Okay Industries to expand an additional 58,000 sq. ft. And in another case, two of three new straightside presses recently added to the East Hanover, NJ, facility of metal former Weiss-Aug are dedicated to specific medical-product lines, including a device used in laser corrective-eye surgery.
Medical-device manufacturers continue exploring and implementing additive manufacturing (AM) in their processes. Expect the worldwide AM prosthetics market to show an 8-percent CAGR from 2023 onward and reach $3.5 billion by 2033, according to Future Market Insights. In 2023, North America will account for 40 percent of worldwide revenue share. MF
View Glossary of Metalforming Terms
See also: Penn United Technologies, Inc., Aida-America Corp.
Technologies: Management








