Page 50 - MetalForming March 2014
P. 50
Tooling by Design
By Peter Ulintz
Forming and Flanging AHSS Material
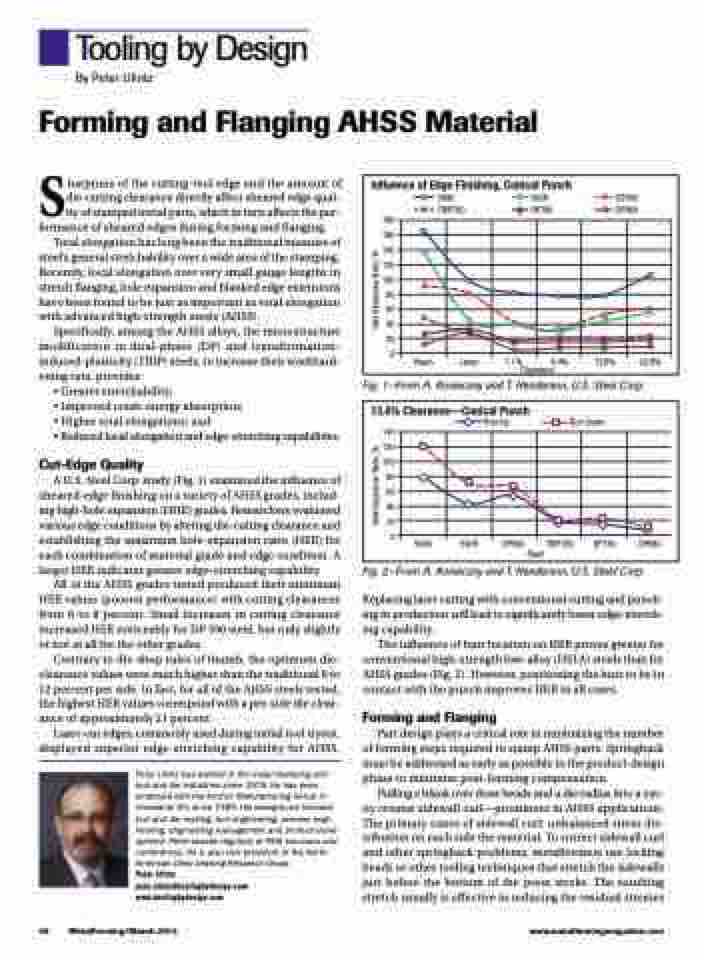
Influence of Edge Finishing, Conical Punch
50XK TRIP780
590R DP780
DP590 DP980
180 160 140 120 100
80 60 40 20
0
Ream
Laser
1.1% Clearance
20.8%
6.4% 13.6%
Sharpness of the cutting-tool edge and the amount of die-cutting clearance directly affect sheared edge qual- ity of stamped metal parts, which in turn affects the per- formance of sheared edges during forming and flanging.
Total elongation has long been the traditional measure of steel’s general stretchability over a wide area of the stamping. Recently, local elongation over very small gauge lengths in stretch flanging, hole expansion and blanked edge extensions have been found to be just as important as total elongation with advanced high-strength steels (AHSS).
Specifically, among the AHSS alloys, the microstructure modification in dual-phase (DP) and transformation- induced-plasticity (TRIP) steels, to increase their workhard- ening rate, provides:
• Greater stretchability;
• Improved crash-energy absorption;
• Higher total elongations; and
• Reduced local elongation and edge-stretching capabilities.
Cut-Edge Quality
A U.S. Steel Corp. study (Fig. 1) examined the influence of sheared-edge finishing on a variety of AHSS grades, includ- ing high-hole expansion (HHE) grades. Researchers evaluated various edge conditions by altering die-cutting clearance and establishing the maximum hole-expansion ratio (HER) for each combination of material grade and edge condition. A larger HER indicates greater edge-stretching capability.
All of the AHSS grades tested produced their minimum HER values (poorest performance) with cutting clearances from 6 to 8 percent. Small increases in cutting clearance increased HER noticeably for DP 590 steel, but only slightly or not at all for the other grades.
Contrary to die-shop rules of thumb, the optimum die- clearance values were much higher than the traditional 8 to 12 percent per side. In fact, for all of the AHSS steels tested, the highest HER values correspond with a per-side die clear- ance of approximately 21 percent.
Laser-cut edges, commonly used during initial tool tryout, displayed superior edge-stretching capability for AHSS.
Peter Ulintz has worked in the metal stamping and tool and die industries since 1978. He has been employed with the Anchor Manufacturing Group in Cleveland, OH, since 1989. His background includes tool and die making, tool engineering, process engi- neering, engineering management and product devel- opment. Peter speaks regularly at PMA seminars and conferences. He is also vice president of the North American Deep Drawing Research Group.
Peter Ulintz pete.ulintz@toolingbydesign.com www.toolingbydesign.com
Fig. 1—From A. Konieczny and T. Henderson, U.S. Steel Corp.
13.6% Clearance—Conical Punch
140 120 100
80 60 40 20
0
Burr Up
50XK 590R DP590
Burr Down
TRIP780 DP780
DP980
Steel
Fig. 2—From A. Konieczny and T. Henderson, U.S. Steel Corp.
Replacing laser cutting with conventional cutting and punch- ing in production will lead to significantly lower edge-stretch- ing capability.
The influence of burr location on HER proves greater for conventional high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels than for AHSS grades (Fig. 2). However, positioning the burr to be in contact with the punch improves HER in all cases.
Forming and Flanging
Part design plays a critical role in minimizing the number of forming steps required to stamp AHSS parts. Springback must be addressed as early as possible in the product-design phase to minimize post-forming compensation.
Pulling a blank over draw beads and a die radius into a cav- ity creates sidewall curl—prominent in AHSS applications. The primary cause of sidewall curl: unbalanced stress dis- tribution on each side the material. To correct sidewall curl and other springback problems, metalformers use locking beads or other tooling techniques that stretch the sidewalls just before the bottom of the press stroke. The resulting stretch usually is effective in reducing the residual stresses
48 MetalForming/March 2014
www.metalformingmagazine.com
Hole Expansion Ratio, % Hole Expansion Ratio, %