Page 53 - MetalForming April 2016
P. 53
Fig. 3—The rate of climb from yield to tensile strength denotes the magnitude of the n-value. Coil #3 has more stretchability than the other two steels.
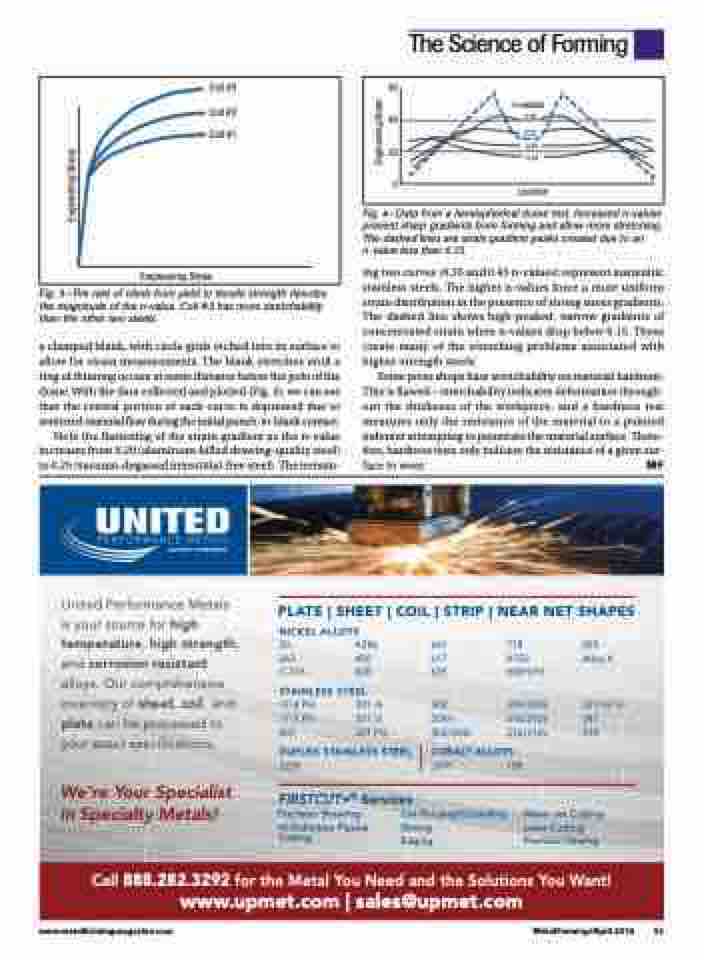
a clamped blank, with circle grids etched into its surface to allow for strain measurements. The blank stretches until a ring of thinning occurs at some distance below the pole of the dome. With the data collected and plotted (Fig. 4), we can see that the central portion of each curve is depressed due to restricted material flow during the initial punch-to-blank contact.
Note the flattening of the strain gradient as the n-value increases from 0.20 (aluminum-killed drawing-quality steel) to 0.25 (vacuum-degassed interstitial-free steel). The remain-
Fig. 4—Data from a hemispherical dome test. Increased n-values prevent sharp gradients from forming and allow more stretching. The dashed lines are strain gradient peaks created due to an n-value less than 0.15.
ing two curves (0.35 and 0.45 n-values) represent austenitic stainless steels. The higher n-values force a more uniform strain distribution in the presence of strong stress gradients. The dashed line shows high-peaked, narrow gradients of concentrated strain when n-values drop below 0.15. These create many of the stretching problems associated with higher-strength steels.
Some press shops base stretchability on material hardness. This is flawed—stretchability indicates deformation through- out the thickness of the workpiece, and a hardness test measures only the resistance of the material to a pointed indenter attempting to penetrate the material surface. There- fore, hardness tests only indicate the resistance of a given sur- face to wear. MF
The Science of Forming
Coil #2 Coil #1
Engineering Strain
Coil #3
60 40 20
0
n-values
0.20 0.25 0.35
0.45
Location
United Performance Metals is your source for high temperature, high strength, and corrosion resistant alloys. Our comprehensive inventory of sheet, coil, and plate can be processed to your exact specifications.
We’re Your Specialist in Specialty Metals!
PLATE | SHEET | COIL | STRIP | NEAR NET SHAPES
NICKEL ALLOYS
20 A286 263 400 C-276 600
STAINLESS STEEL
17-4 PH 301 1⁄4 17-7 PH 301 1⁄2 301 301 FH
DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL
2205
FIRSTCUT+® Services
601 718
617 X750 625 800H/HT
302 309/309S 304H 310/310S 304/304L 316/316L
825 Alloy X
321/321H 347
410
COBALT ALLOYS
L605 188
Precision Shearing
Hi-Definition Plasma Cutting
Cut-To-Length/Leveling Slitting
Edging
Water Jet Cutting Laser Cutting Precision Sawing
Call 888.282.3292 for the Metal You Need and the Solutions You Want! www.upmet.com | sales@upmet.com
www.metalformingmagazine.com
MetalForming/April 2016 51
Engineering Stress
Engineering Strain