Page 58 - MetalForming-Apr-2018-issue
P. 58
New Steels:
A new model yields results that should continue the trend of AHSS as the fastest growing material in automotive applications.
BY DAVID ANDERSON
As the automotive
industry works to
meet increasingly
stringent fuel economy
and safety regulations,
the steel industry contin-
ues to collaborate with
automakers to innovate
and implement advanced high-strength steels (AHSS)
into new vehicle designs. AHSS is the fastest growing material in automotive applications, according to a 2015 report by Ducker Worldwide, showing that the amount of AHSS used annually in automotive applications has totaled 10 percent higher than forecast during the past three years.
A testament to the industry’s interest in AHSS, in particular third-generation AHSS (3rd-Gen AHSS), the United States Automotive Materials Partner- ship LLC (USAMP), a wholly owned subsidiary of the U.S. Council for Auto- motive Research LLC representing FCA US LLC, Ford Motor Co. and General Motors, completed a four-year project in 2017. This project worked to develop an Integrated Computational Materials
David Anderson is senior director, auto- motive program, at Steel Market Devel- opment Institute, Washington, D.C.; 202/452-7100, www.smdisteel.org.
Collaboration Leads to Lightweighting
200 160 120
80 40 0
200+
80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10
0
Aluminum Alloys
Yield Strength vs. Elongation %
CONVENTIONAL STEELS
AHSS GRADES
IF
IF-HS
Mild BH
MS
MnB+ HF
TODAY
200 500
800 1100 1400 Tensile Strength (MPa)
1700 2000
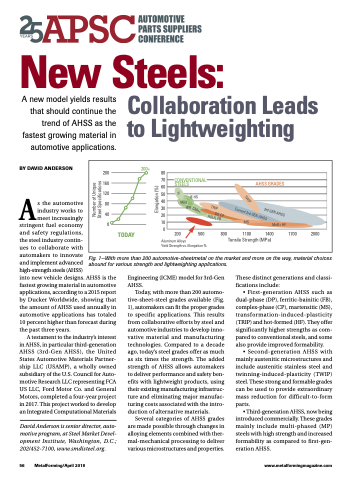
Fig. 1—With more than 200 automotive-sheetmetal on the market and more on the way, material choices abound for various strength and lightweighting applications.
Engineering (ICME) model for 3rd-Gen AHSS.
Today, with more than 200 automo- tive-sheet-steel grades available (Fig. 1), automakers can fit the proper grades to specific applications. This results from collaborative efforts by steel and automotive industries to develop inno- vative material and manufacturing technologies. Compared to a decade ago, today’s steel grades offer as much as six times the strength. The added strength of AHSS allows automakers to deliver performance and safety ben- efits with lightweight products, using their existing manufacturing infrastruc- ture and eliminating major manufac- turing costs associated with the intro- duction of alternative materials.
Several categories of AHSS grades are made possible through changes in alloying elements combined with ther- mal-mechanical processing to deliver various microstructures and properties.
These distinct generations and classi- fications include:
• First-generation AHSS such as dual-phase (DP), ferritic-bainitic (FB), complex-phase (CP), martensitic (MS), transformation-induced-plasticity (TRIP) and hot-formed (HF). They offer significantly higher strengths as com- pared to conventional steels, and some also provide improved formability.
• Second-generation AHSS with mainly austenitic microstructures and include austenitic stainless steel and twinning-induced-plasticity ( TWIP) steel. These strong and formable grades can be used to provide extraordinary mass reduction for difficult-to-form parts.
• Third-generation AHSS, now being introduced commercially. These grades mainly include multi-phased (MP) steels with high strength and increased formability as compared to first-gen- eration AHSS.
56 MetalForming/April 2018
www.metalformingmagazine.com
Number of Unique Steel Specifications
Elongation (%)
TWIP
TRIP
CMn+
3rd GEN AHSS Current 3rd GEN AHSS
DP, CP
HSLA, FB